1) Martolis Pieters (9O)
WT's Need a wide open, flat and obstacle free view (sweeping area) in the prevailing wind direction.
Windspeed is influenced by contours of local terrain.
Large WT's needs to connect to an electrical grid.Small WT's need to be close to a 10-30kilovolt powerline.
The powergrid may need to be reinforced if multiple Wt's are connected to it.
Soil conditions requires accessability of heavy machines as well as solid substrata.
2) Annette van der Merwe (90)
The common way is placement on hills or ridges overlloking the surrounding landscape facing the prevailing wind direction.
Hills have higher wind speeds because wind becomes compressed on the windward side of the hill when the air reaches the ridge it can expand again as it flows down into the low pressure area.
If the hill is steep or has an uneven surface turbulence is common which may negate the advantage of higher wind speeds.
3) YC - (90)
Noise 2 types of Noise: Aerodynamic sound (reduced by micro processor) Mechanical sound (battery charging capability reduces flutter) Sound increases with bade speed. Shape of blade determines the type of noise.
WT's Need a wide open, flat and obstacle free view (sweeping area) in the prevailing wind direction.
Windspeed is influenced by contours of local terrain.
Large WT's needs to connect to an electrical grid.Small WT's need to be close to a 10-30kilovolt powerline.
The powergrid may need to be reinforced if multiple Wt's are connected to it.
Soil conditions requires accessability of heavy machines as well as solid substrata.
2) Annette van der Merwe (90)
The common way is placement on hills or ridges overlloking the surrounding landscape facing the prevailing wind direction.
Hills have higher wind speeds because wind becomes compressed on the windward side of the hill when the air reaches the ridge it can expand again as it flows down into the low pressure area.
If the hill is steep or has an uneven surface turbulence is common which may negate the advantage of higher wind speeds.
3) YC - (90)
Noise 2 types of Noise: Aerodynamic sound (reduced by micro processor) Mechanical sound (battery charging capability reduces flutter) Sound increases with bade speed. Shape of blade determines the type of noise.
4) Gous Germishuys (9C)
Factors Influencing Placement:
-Wind availability
-Wind speed
-Turbulence
-Availability of transmission lines
-Energy produced
-Municipal Laws
-Cost of land acquisition
-Land use considerations
-Environmental impact of construction and operations.
-Soil type-Rocks under soil
What wind turbines require:
For a wind turbine to produce power and for that power to reach our school our wind turbine(s) need:
-To be close to a main power line
-Constant wind as well as winds with adequate wind speeds (depending on the turbine)
-To be at least 10m above any obstruction within a 100m radius of the turbine (including trees)
-As little turbulence as possible because turbulence puts strain on all the parts in a generator
-No objects blocking wind direction to the wind turbine
-Tower must have a “fall-zone” that does not impact any neighbouring property
-Large open spaces
Ideal wind turbine position:
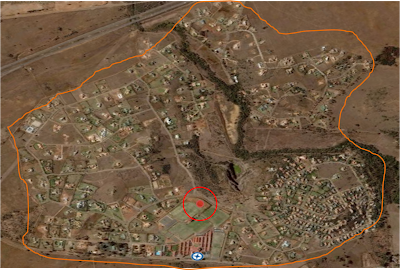
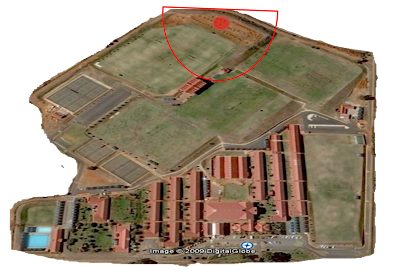
If a wind turbine was to be built on the Cornwall Hill College property or in the Cornwall Hill Estate, there would be many problems because of the nearby military air-force base. Although if permission is granted, the wind turbine could be built at this possible location.
-The corner of the school --Geographical co-ordinates ----25°52’28.64”S 28°14’16.27”E
(See photos at the start of the section)
- Because there are no classrooms + buildings nearby to be affected by noise pollution, except when there is sport at those fields. It is the flattest area, with more than 100m radius.
-I have no information on the soil in that area nor information about power lines in that area.
Thshepiso Mabusela (9R)
Kamilla Snyman (9A)
Emilie Niewoudt (9O)
Chante De Klerk (9A)
Gavin Badenhorst (9C)
Jaimie Fouche (9C)
Jonathan Wocke (9N)
Herman de Klerk (9A)
Nico Till (9A)
Aiden Markram (9N)





No comments:
Post a Comment